〠Instrument R & D of Instrumentation Network 】 Recently, Xiao Chunlei, Sun Zhigang, a researcher from Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Zhang Donghui and Yang Xueming, academicians of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in the simple chemical reaction hydrogen atom hydrogenation molecule isotope (H + HD → H2 + D) reaction, New quantum interference effects in chemical reactions are discovered, which helps to understand the chemical reaction process more deeply and enrich the understanding of chemical reactions.
In chemical reactions, quantum interference phenomena are ubiquitous. However, it is very difficult to accurately understand the root cause of these interferences, because the patterns of these interferences are complex, and it is difficult to accurately distinguish the characteristics of these interference patterns experimentally.
The reaction of H + H2 and its isotopes is simple in all chemical reactions. The system involves only three electrons, so it is easier to accurately calculate the interaction force of the three atoms in different configurations. On this basis, by solving the corresponding Schrodinger equation describing the chemical reaction process, it is possible to realize the computer simulation of the molecular reaction dynamics process, so as to achieve a deep understanding of the chemical reaction process at the micro level. The research team found in the preliminary theoretical research work in 2019 that at a specific scattering angle, the amount of H2 produced by the H + HD reaction will show a particularly regular oscillation with the collision energy.
Schrödinger equation, also known as Schrodinger wave equation, is a basic equation in quantum mechanics proposed by Austrian physicist Schrodinger wave equation, and is also a basic assumption of quantum mechanics.
It is a second-order partial differential equation established by combining the concept of matter waves and wave equations. It can describe the movement of microscopic particles. Each microscopic system has a corresponding Schrodinger equation. The specific form of the wave function can be obtained by solving the equation and Corresponding energy to understand the nature of the micro system. The Schrödinger equation shows that in quantum mechanics, particles appear in a probabilistic manner, with uncertainty, and failure at a macroscopic scale is negligible.
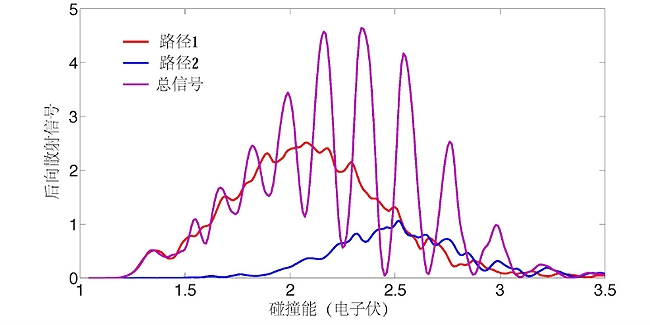
In response to this regular oscillation phenomenon, the team carried out a detailed study of the combination of theory and experiment. Experimentally, through the improved cross molecular beam device, accurate measurement of the backscattering signal (scattering angle of 180 degrees) at high collision energy was achieved. Theoretically, the quantum reaction scattering theory has been further developed, and the method of analyzing the way of chemical reaction using the principle of topology has been creatively developed.
Topological analysis shows that these backscattered oscillations are actually caused by the interference of two reaction pathways. Both of these two reaction pathways contribute significantly to backscatter, but their respective amplitudes do not change significantly with the change of collision energy, showing a slow trend. Their phases change with the collision energy, one increases linearly and the other decreases linearly. Therefore, the result of mutual interference presents a strong and regular oscillation phenomenon.
Topology is a discipline that studies some properties of geometric shapes or spaces that can remain unchanged after continuously changing shapes. It only considers the positional relationship between objects without considering their shape and size.
Topology's English name is Topology, and literal translation is topography, which first refers to related subjects that study similar topography and topography. Geometric topology is a branch of mathematics formed in the 19th century. It belongs to the category of geometry. Some content about topology appeared as early as the eighteenth century. Some isolated problems discovered at that time played an important role in the formation of later topology.
Further analysis using classical trajectory theory shows that one of the reaction pathways corresponds to the commonly known direct reaction process. The other reaction path corresponds to a reaction process similar to roaming mechanism. Since these two reaction paths happen to surround the conical intersection on the potential energy surface of the H + HD reaction in opposite directions, their interference patterns must be simulated using non-adiabatic potential energy surfaces. Geometric phase effect during the reaction of the system. It is particularly interesting that in the range of collision energies studied, the reactions that occur through the roaming mechanism account for only about 0.3% of the total reactivity. And such a small part of the reactivity can be clearly revealed by theory and experiment.
This study on the one hand revealed the quantum nature of the chemical reaction process of atomic molecules due to collision, on the other hand, it also revealed that the way of chemical reaction is complicated. Nevertheless, the simple system still has the fact that scientists do not recognize it.
Source: Encyclopedia, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics
Oil Can Lid,Tinplate Caps,Metal Press Caps,Plastic Spout Lid
Jiangsu Fast Pack Co., Ltd , https://www.fastmetalpack.com