A method goethite iron principle of a goethite structure and thermodynamic stability is one of the goethite iron oxide mineral water, often referred to [alpha] type - water iron oxide, its composition is α - Fe 2 0 3 · H 2 0 or Fe00H, which is a homomorphic variant with fibrite ( γ- Fe00H).
From the point of view of modern chemistry, goethite belongs to the category of inorganic polymers. The unit represented by the formula Fe00H does not exist independently. The formula of goethite should be written as [ α -Fe00H] n , where n is a relatively large number, and the high-iron ion at the center of the octahedron has a strong polarization ability, which enables the outer electrons of the surrounding coordination ions. The cloud is deviating. The outer electron clouds of the positive and negative ions overlap each other and form a covalent bond.
Oxidation-reduction potential and pH are two important factors controlling the behavior of iron in aqueous solution. The oxidizing environment promotes the precipitation of iron, which reduces the dissolution of iron. Acidic conditions generally favor iron dissolution and alkaline conditions promote iron precipitation. The chemical reaction of goethite in aqueous solution is:
Fe00H+(3-n) H + ==== Fe(OH) n (3-n)+ +(2-n) H 2 0
Assuming that both the solid phase and the water activity are equal to 1, the equilibrium constant K 0 = α Fe(OH) n (3-n) + / α H+ (3-n) , ( where n = 0, 1, 2, 3 , 4). and so:
Lg α Fe(OH) n (3-n) + = lgK 0 - (3 - n)pH
The table below lists the equilibrium constant values ​​for goethite-related reactions. It can be seen that as the acidity of the aqueous solution decreases, the content of Fe 3+ ions in the solution decreases remarkably, that is, the value of 1 g K 0 decreases.
Related parameters of goethite dissolution reaction | ||||||
reaction | Lg α Fe ( III ) | Lg α Fe ( III ) | LgK 0 298 | LgK 0 368 | LgK 0 413 | |
PH | ||||||
FeOOH+3H + === Fe 3+ +2H 2 O | LgK 0 -3pH | -3 | 3.96 | 1.15 | -0.63 | |
FeOOH+2H + === FeOH 2+ +H 2 O | LgK 0 -2pH | -2 | 0.94 | -0.51 | -1.44 | |
FeOOH+H + === Fe ( OH ) 2 + | LgK 0 -pH | -1 | -2.38 | -2.9 | -3.24 | |
FeOOH+H 2 O === Fe ( OH ) 3 | LgK 0 | 0 | -6.53 | -5.36 | -4.61 | |
FeOOH+ 2H 2 O === Fe ( OH ) 4 - +H + | LgK 0 -pH | 1 | -18.72 | -18.556 | -18.45 | |
FeOOH+4H + == Fe 2 ( OH ) 2 4+ +2H 2 O | 1 | Â LgK 0 -2pH Â | -1 | 5.58 | 1.21 | -1.6 |
| 2 | ||||||
The chromatite solubility curve plotted based on the calculated values ​​of the equilibrium constants listed in the table above is shown in the figure below. The dotted line in the figure indicates the main existence interval of the complex ions, and the solid line indicates the solid phase line. Below the solidus line, the solution is stable and there is no precipitation of goethite; above the solidus line, the solution is unstable and goethite tends to precipitate. The change in complex ions is gradual. The concentration of two adjacent ions on the dotted line is equal, and when pH < 3, the equilibrium concentration of Fe 3+ ions changes very rapidly; when pH > 3, when [SO 4 2- ] < 0.1 mol/dm 3 , It has little effect on the solubility of goethite.

b High-valent iron ion reduction The amount of Fe 3+ removed from an aqueous iron solution depends on the solubility of the precipitate. The presence and transformation process of the precipitate can be illustrated as follows:

The newly precipitated hydroxide consists of a number of compounds whose solubility is governed by the most soluble compound in the mixture. "Active" means that the solid is transformed, and the newly precipitated active amorphous Fe(OH) 3 is slowly converted into goethite crystals and a relatively stable amorphous hydroxide, and the conversion is completed at 100 ° C for about one day. This is not easy to achieve for general industrial operations, and the final product after conversion is still a mixture containing a large amount of Fe(OH) 3 . Therefore, it is important to select a good goethite precipitation condition to obtain a pure, easily filtered precipitate. An in-depth study of the precipitation conditions of a single iron compound from a thermodynamic point of view can be represented by the Fe 2 0 3 -S0 3 -H 2 0 system, and it is shown that only when the concentration of Fe 3+ in the sulfate solution is very low, Forming goethite deposits. [next]

Application Method B goethite in a wet zinc smelting plant Babylon Belgium leached wet processing method using goethite, which is the flowchart as shown below. The figure shows that it is a combination of the float method and the old method. The new method is leaching slag in acid leaching, and the iron leaching solution is used to remove iron by the goethite method.
 [next]
[next]
Neutral leaching residue using 50g / dm 3 sulfuric acid leach, the extraction rate of each metal were Zn 80%, Cu 85%, Fe 80%, Cd 90% at 85 ℃ leaching at 6h, resulting infusion containing Zn60g / dm 3, Fe 3+ 25 g/dm 3 , H 2 SO 4 50 g/dm 3 and Cu, Cd, As, Ga, Ni, Co and the like. The iron is removed by goethite method. In order to keep Fe 3+ in the sedimentation liquid less than 1 g/dm 3 , the balun plant uses sphalerite as a reducing agent. Operating temperature 90 ~ 95 ° C, time 6 ~ 8h. Generally, the amount of reducing agent added needs to be 15% to 20% in excess. The calcination is used as a neutralizing agent, and the neutralization reaction takes about 1 hour to reduce the acidity from 50 g/dm 3 to 2 to 3 g/dm 3 . Low iron oxidation uses air or oxygen. If the pH of the solution is increased from 2.2 to 3.5, the goethite precipitation rate is doubled. The effect of alkali metal sodium ions on the sinking iron is shown in the figure below. It indicates that the sodium ion content is less than 2g/dm 3 , and if the precipitation pH is >2, there is no effect on the goethite precipitation; if the pH is 4.0, a part of α- Fe 2 0 3 will be formed. For the calcined ore containing 57% zinc and 8% iron, the zinc lost with the iron ore slag is about 1.4% to 2.8%, and the composition of the obtained goethite slag is: Fe 41.35%, Zn 8.5%, Pb 2.2%, Ag. 0.0119%, Cd 0.05%, Cu 0.5%, As 0.54%, Sb 0. 067%, Sn 0.06%, Co 0.0118%, Ni 0.0101%, K 0.17%, Na 0.07%.

The Orville Pate Metallurgy Company in Hobken, Belgium is a 100 kt zinc wet zinc smelting plant that was commissioned in May 1974 (120 kt in 1985). The residue was treated with goethite, and the flow is shown in the figure below. Neutral leaching, in addition to dissolving zinc, is also aimed at precipitating iron by hydrolysis and removing a range of harmful impurities. Therefore, the divalent iron ions originally present in the solution and brought back from the solution returned from the goethite operation are blasted into the air at the bottom of the stirred leaching tank, and the solid matter is separated in the dense tank and then leached with a weak acid having a pH of 3. To dissolve more zinc, copper , tin . The leaching residue contains zinc ferrite, lead , silver and an inert substance. The two-stage countercurrent system leached by hot acid and superheated acid dissolves almost all of zinc and iron when the final acid concentration of the superheated acid leaching reaches 120 g/dm 3 . The final slag contains lead, silver and most of the silica and calcium oxide. After the resulting solution was twice leached zinc containing about l00g / dm 3, Fe 25 ~ 30g / dm 3, acid 50 ~ 60g, / dm 3. ZnS is used as a reducing agent, and the reduced liquid still contains 50 to 60 g/dm 3 of sulfuric acid, and neutralized with calcined to 3 to 5 g/dm 3 of acid. The goethite precipitation is carried out at 90 ° C and a pH of 3, air is used as an oxidant, and the composition of goethite slag is shown in the table below. [next]

Typical analysis of leaching residue | |||
element | Pb/Ag residue | S residue | Goethite slag |
Zn | 1.5 to 3.0 | 8~5 | 5~9 |
Fe | 3 to 5 | 7~8 | 40~42 |
Pb | 25~30 |   |   |
Ag | 0.1 to 0.15 |   |   |
SiO2 | 10~14 |   | 2 |
CaO | 2 to 6 |   | 0.7 |
Total S | 15~20 | 50 | 4 |
Element S |   | 0~35 |   |
Because the "V. M" method developed by Laoshan Company has two processes of reduction and oxidation, it is more troublesome to operate. In order to simplify the process, the partial hydrolysis method (ie E. Z) developed by the Australian Electric Zinc Company has been studied and applied at home and abroad. The "E. Z" method of production drunk is the control of the spray method and the zinc content of the iron slag, that is, how to increase the spray speed and reduce the zinc content of the iron slag. With the "E. Z" method, iron can be removed quickly and efficiently, and the sedimentation and filtration of the iron slag and the decontamination performance of the iron removal liquid are good.
In front of Zhongzhu University of China, Mei Guanggui and others proposed the goethite method for zinc sulfite reduction. On the basis of small test, pilot test and industrial test, it was trial production by Shuikoushan No.4 Plant. At present, in addition to Wenzhou smelting plant and Shuikoushan No. 4 plant in China, there has not been more popularization and application in wet zinc smelting, but it has been applied in other metal wet process iron removal. It should be recognized that The process is an advanced method, especially in the process of extracting indium by extraction method, which is more advantageous [1] and is expected to be further popularized and applied in China in the future.
references:
1 Ma Rongjun, "Hydrometallurgy" 1997, No. 1: 59-61.
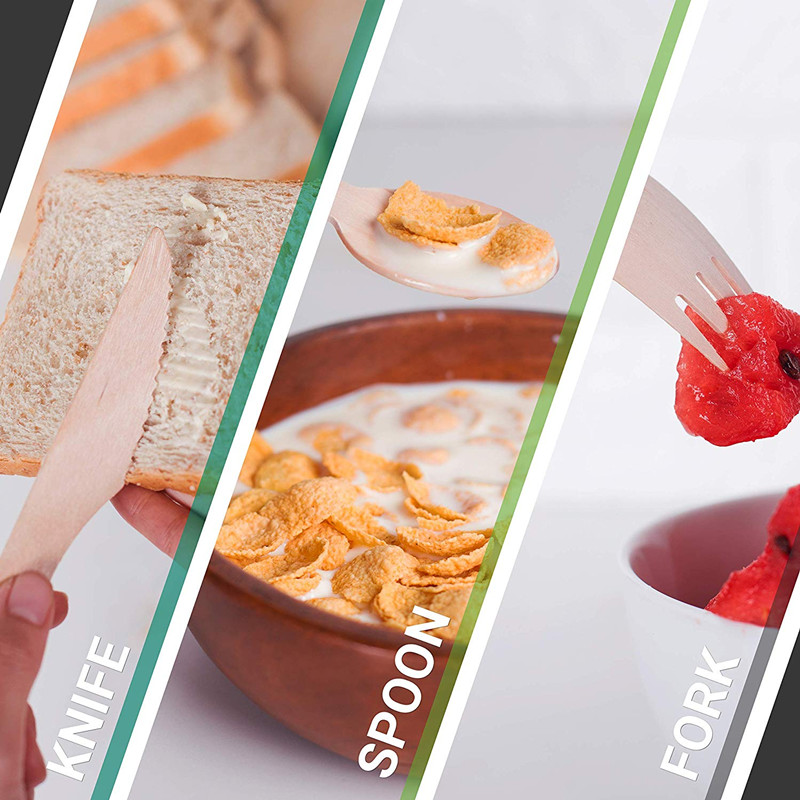
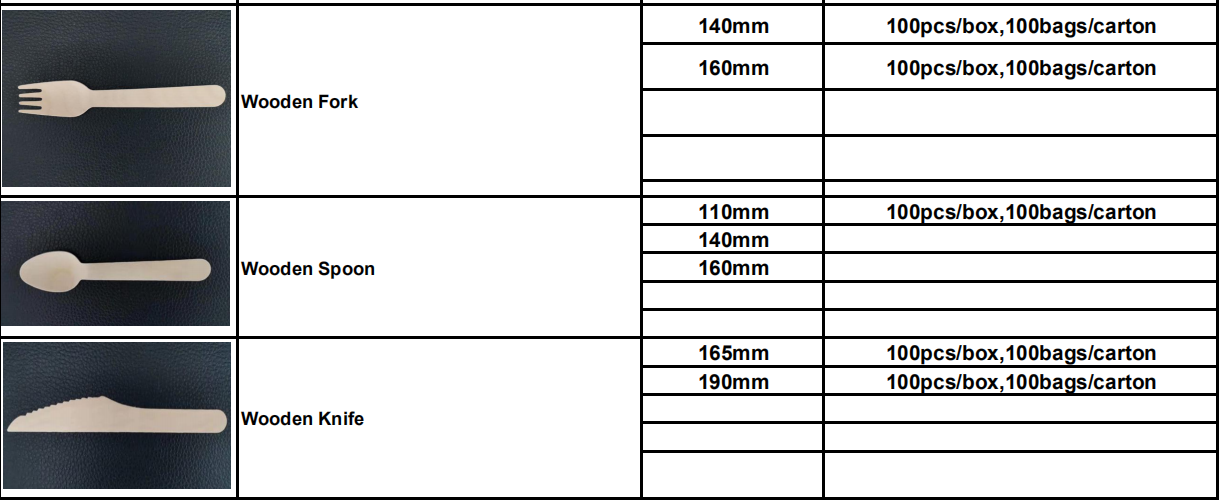
Disposable kitchenware


FAQ
Q1: Are you manufacturer or trading company?
A1: We are manufacturer.
Q2: What is the material of products?
A2: Natural Birch.
Q3: How long will you deliver the products?
A3: 30~60 days after receiving 30% T/T deposit.
Q4: What is the payment term?
A4: T/T 30% as deposit in advance and balance 70% should be paid when goods ready to ship or L/C at sight.
Q5: Do you provide samples?
A5:Yes, free samples available.
Disposable Kitchenware,Disposable Wood Cutlery,Disposable Wood Eating Utensils,Wood Disposable Cutlery
Dalian Yongtailong Wood Industry Co.,Ltd , https://www.ytldisposablegoods.com